Reactive Airway Disease Child
Reactive airway disease child. It is common for infants and children to cough and wheeze when they have a cold. Bronchospasm is a symptom not a diagnosis. A child affected by the disease starts breathing fast and shallow.
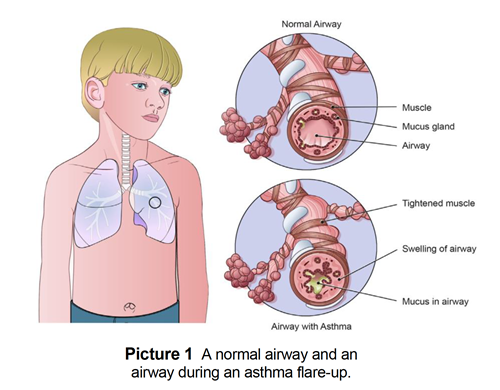
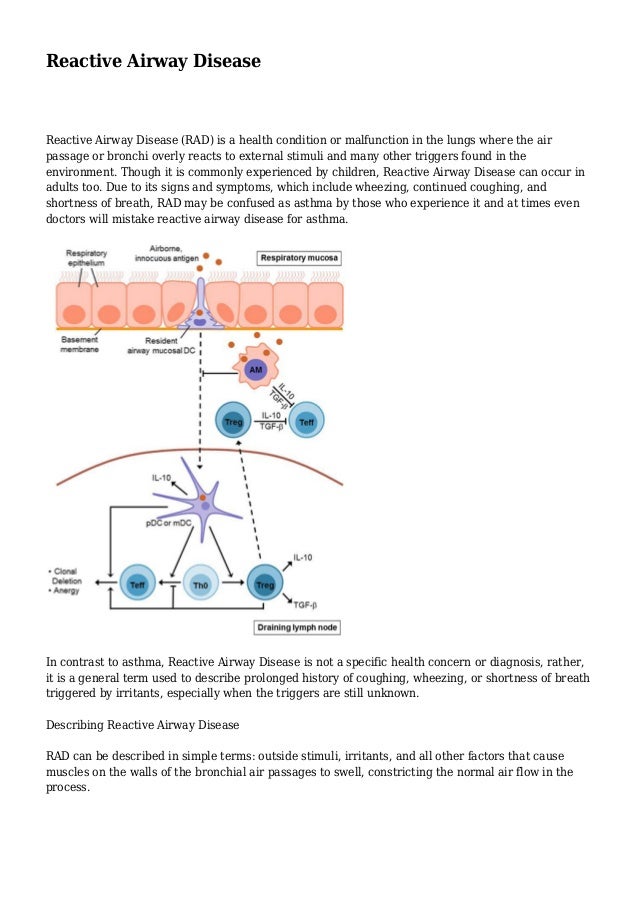
The term reactive airway disease originally began to appear in medical literature in the 1980s in reference to asthmatic patients with hyperactive airways which is a common feature of asthma. This is called a flare-up. Children with pre-school wheeze have sensitive airways.
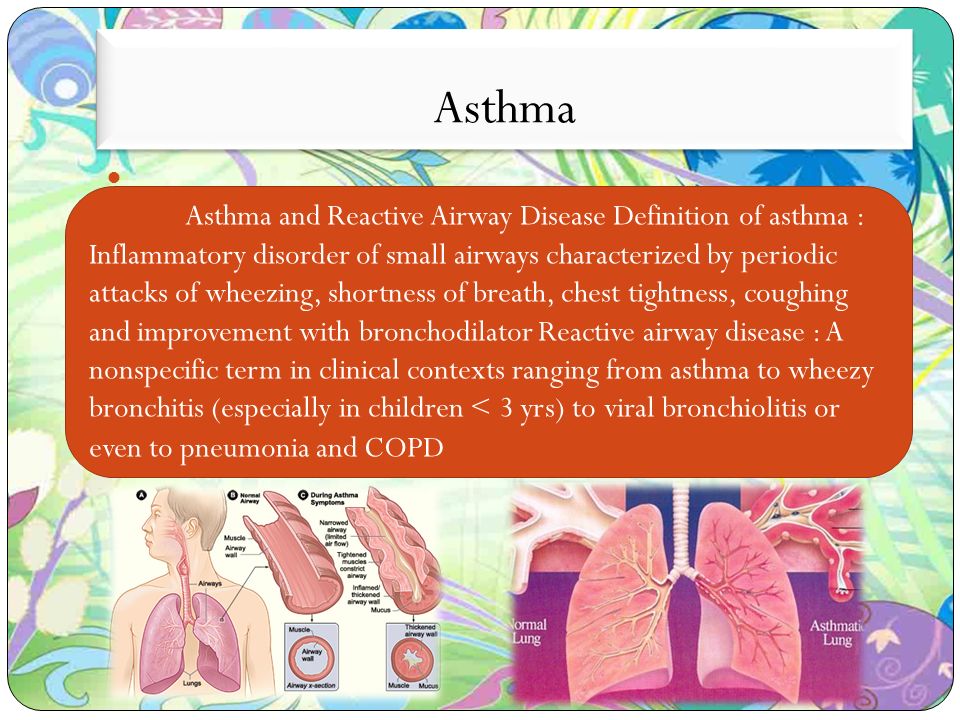
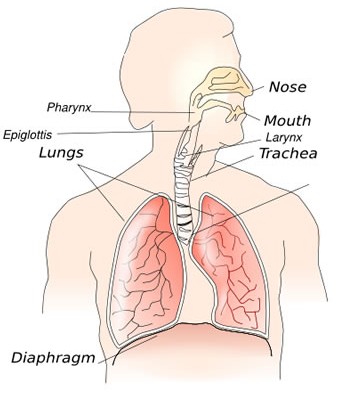
The airways may get smaller when you are around things that trigger your asthma. The major symptom of reactive airway disease is wheezing which is triggered by passage of the air through the narrow airways. Risk Factors of Reactive Airway Disease.
A presentation like this is frequently heard on pediatric units despite the vagueness of the term reactive airways disease commonly referred to as RAD The term is often used as a substitute for asthma in young children on asthma medications when pediatricians are reticent to use the A word. Bronchospasm is a narrowing of the airways after contact with a trigger. The overreaction of the airway to a trigger may be called reactive airway disease.
This may be from a viral or bacterial infection. Children under the age of 5 are typically diagnosed with RAD since it can be. A Child with Presumed Reactive Airway Disease Pectus Carinatum and Aortic Root Dilation.
This disease is caused by aerial pollutants and is non-contagious. Dry cough is present too. It is a term that may be used for a 1-time event or as a holder until a diagnosis can be made.
Your Care Instructions Bronchoconstriction which may also be called reactive airway disease occurs when the small airways bronchial tubes in your childs lungs spasm and become narrow. This feature is characterized by increased bronchoconstriction reactions in response to stimuli that should not elicit so strong of response.
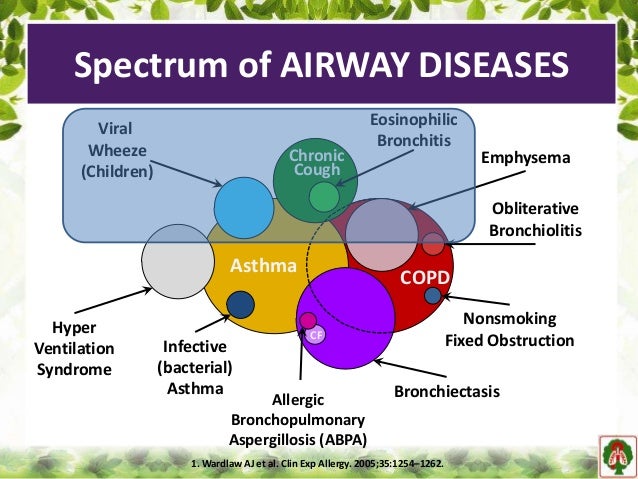
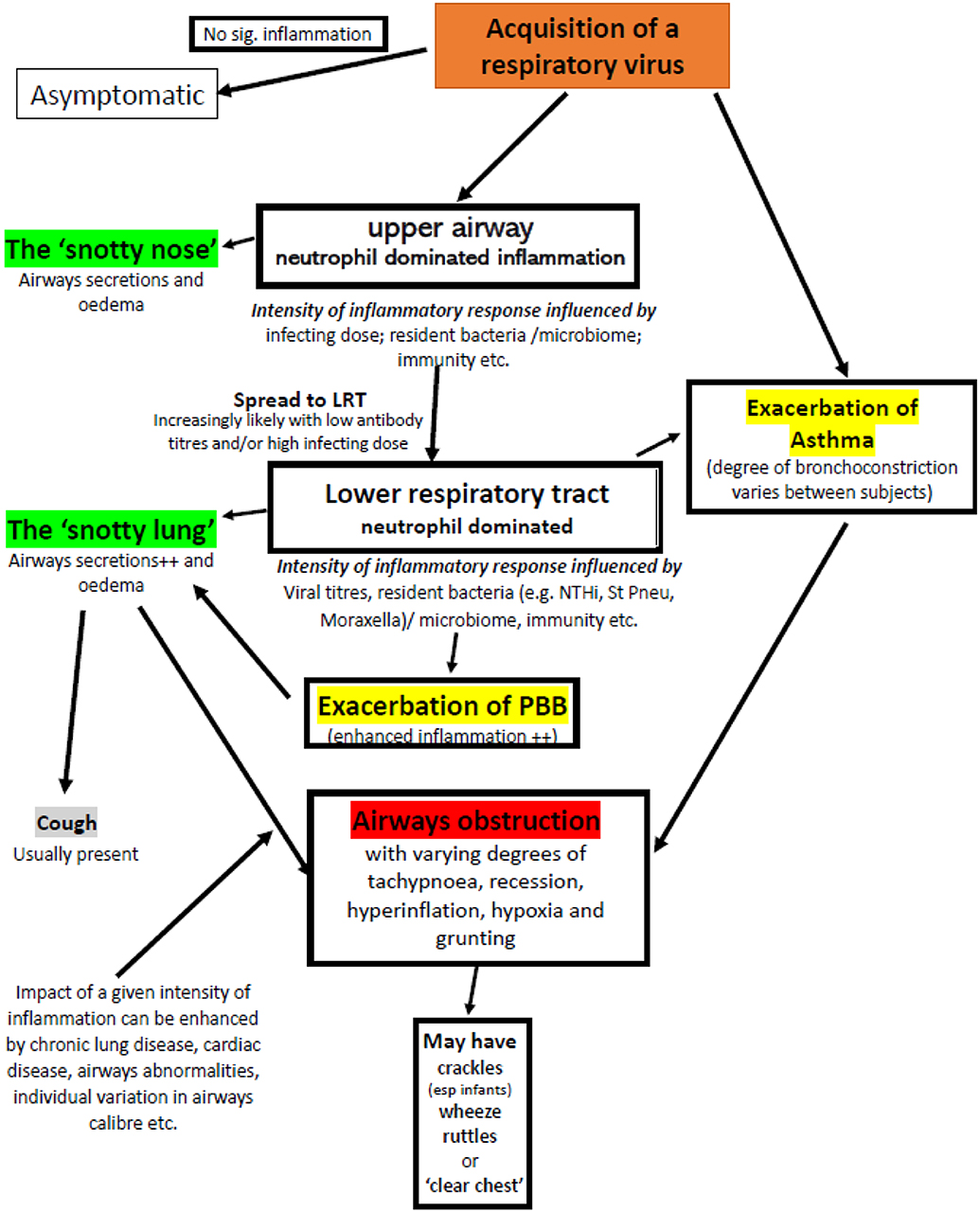
Childhood reactive airway diseases RADs are concerning problems in childrens airways and may be preceded by bronchiolitis and may progress to childhood asthma.
Reactive airway disease in children is caused by infection virus and allergy to environmental stimulus. It is common for infants and children to cough and wheeze when they have a cold. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of asthma. Children with pre-school wheeze have sensitive airways. The major symptom of reactive airway disease is wheezing which is triggered by passage of the air through the narrow airways. The symptoms of RAD are similar to asthma and allergies. It causes wheezing which is a whistling noise in your childs airways. Your Care Instructions Bronchoconstriction which may also be called reactive airway disease occurs when the small airways bronchial tubes in your childs lungs spasm and become narrow. This is called a flare-up.
This disease is caused by aerial pollutants and is non-contagious. Dry cough is present too. Jeewa A Morris SA Dreyer WJ Adachi I Denfield SW McKenzie ED Pediatr Rev 2017 Jan381e1-e5. Reactive airways disease RAD is a term used to describe breathing problems in children up to 5 years old. A child affected by the disease starts breathing fast and shallow. This feature is characterized by increased bronchoconstriction reactions in response to stimuli that should not elicit so strong of response. This is called a flare-up.

















/COPD-56a1977d3df78cf7726c476a.jpg)













Posting Komentar untuk "Reactive Airway Disease Child"